Welcome to the European Bodies of Water Quiz, an engaging journey through the diverse and fascinating aquatic landscapes of Europe. From towering mountains to sprawling plains, this continent boasts a remarkable array of rivers, lakes, and seas, each with its own unique story to tell.
Join us as we explore the geographical distribution, significance, and environmental challenges facing these vital bodies of water. Prepare to test your knowledge and deepen your understanding of Europe’s watery wonders.
European Bodies of Water
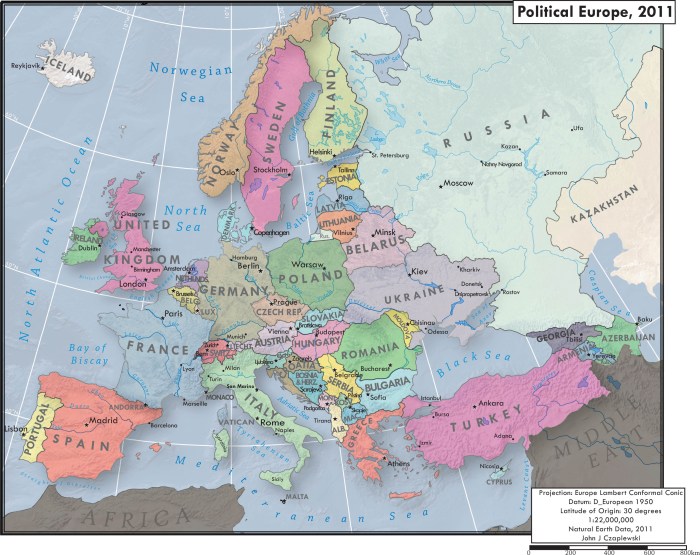
Europe is home to a vast and diverse range of bodies of water, including seas, lakes, rivers, and canals. These bodies of water play a vital role in the European landscape, providing transportation routes, sources of food and water, and recreational opportunities.
The major seas that border Europe include the Atlantic Ocean, the Arctic Ocean, the Baltic Sea, the Black Sea, the Caspian Sea, and the Mediterranean Sea. These seas provide important trade routes and are home to a variety of marine life.
If you’re a geography buff, take our European bodies of water quiz to test your knowledge. Crown Point is a beautiful town that’s nestled on the shores of Lake Champlain, a stunning natural setting . So, how well do you know your European bodies of water? Take the quiz and find out!
Europe is also home to numerous lakes, including Lake Baikal, the largest freshwater lake in the world, and Lake Geneva, one of the most beautiful lakes in Europe. These lakes provide important sources of water for drinking, irrigation, and transportation.
The major rivers of Europe include the Danube, the Rhine, the Volga, and the Thames. These rivers provide important transportation routes and are used for irrigation and hydroelectric power.
Canals are also an important part of the European water system. The most famous canal in Europe is the Suez Canal, which connects the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea. Canals provide important transportation routes and are used for irrigation and flood control.
Types of European Bodies of Water
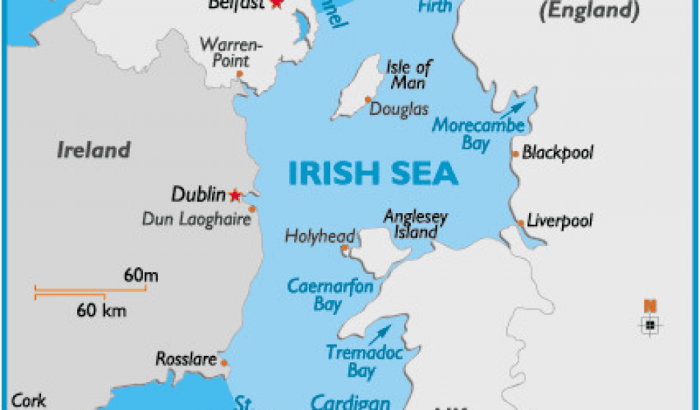
Europe is home to a diverse range of bodies of water, from vast oceans to tranquil lakes and mighty rivers. These water bodies play a crucial role in the continent’s ecology, economy, and culture.
Let’s explore some of the major types of European bodies of water and their notable features:
Seas
| Type | Name | Location | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sea | Mediterranean Sea | Southern Europe | Warm, salty water; home to diverse marine life; important for shipping and tourism |
| Sea | North Sea | Northern Europe | Shallow, cold waters; rich in fish and oil and gas reserves |
| Sea | Black Sea | Eastern Europe | Partially enclosed sea; brackish water; important for fishing and shipping |
Major European Seas
Europe is home to a diverse range of seas, each with its unique characteristics and importance. These seas play a vital role in the continent’s economy, environment, and culture.
Major European Seas
- Mediterranean Sea: Located in southern Europe, the Mediterranean Sea is the largest enclosed sea in the world. It connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the Strait of Gibraltar and is surrounded by numerous countries, including Spain, France, Italy, Greece, and Turkey.
The Mediterranean Sea is a popular tourist destination and an important trade route. It is also home to a diverse range of marine life.
- North Sea: Located in northwestern Europe, the North Sea is bordered by the United Kingdom, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands, and Belgium. It is a major source of oil and gas and is also important for fishing. The North Sea is home to a number of important ports, including Rotterdam and Hamburg.
- Baltic Sea: Located in northern Europe, the Baltic Sea is bordered by Sweden, Finland, Russia, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Germany, and Denmark. It is a relatively shallow sea with a low salinity level. The Baltic Sea is important for fishing and is also a popular tourist destination.
- Black Sea: Located in southeastern Europe, the Black Sea is bordered by Turkey, Bulgaria, Romania, Ukraine, Russia, and Georgia. It is a deep sea with a high salinity level. The Black Sea is important for fishing and is also a major source of oil and gas.
- Adriatic Sea: Located in southern Europe, the Adriatic Sea is bordered by Italy, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, and Albania. It is a relatively narrow sea with a long coastline. The Adriatic Sea is important for tourism and is also a major trade route.
These are just a few of the many seas that are found in Europe. Each sea has its own unique characteristics and importance, and they all play a vital role in the continent’s economy, environment, and culture.
European Lakes
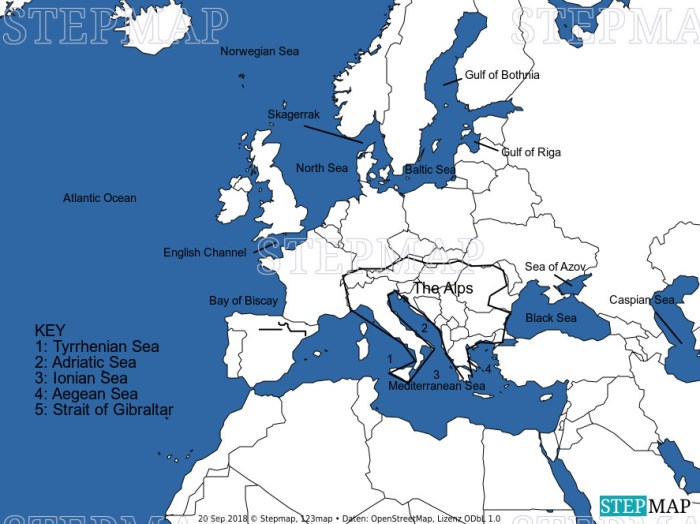
Europe is home to a multitude of captivating lakes, each boasting unique geological formations and ecological significance. These aquatic wonders serve as recreational and tourist hotspots, attracting nature enthusiasts and adventure seekers alike.
Largest European Lakes
- Lake Ladoga (Russia):The largest freshwater lake in Europe, renowned for its vast expanse and numerous islands.
- Lake Onega (Russia):The second-largest lake in Europe, featuring a picturesque archipelago and significant historical importance.
- Lake Vänern (Sweden):The largest lake in Sweden, known for its pristine waters and stunning islands.
- Lake Saimaa (Finland):The fourth-largest lake in Europe, renowned for its intricate labyrinth of waterways and rich biodiversity.
Geological Formations
European lakes exhibit diverse geological origins, including:
- Glacial lakes:Formed by the erosion of glaciers, these lakes often feature steep sides and deep basins, such as Lake Como in Italy.
- Tectonic lakes:Created by tectonic plate movements, these lakes occupy deep depressions or rift valleys, such as Lake Baikal in Russia.
- Volcanic lakes:Formed in craters or calderas of extinct volcanoes, these lakes often possess unique water chemistry and mineral-rich waters, such as Lake Myvatn in Iceland.
Ecological Significance
European lakes play a crucial role in the ecosystem, providing habitats for a wide range of flora and fauna. They serve as:
- Biodiversity hotspots:Supporting diverse communities of fish, birds, and aquatic plants.
- Water reservoirs:Regulating water flow and providing drinking water sources for nearby communities.
- Carbon sinks:Absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and contributing to climate change mitigation.
Recreational and Tourism Value
The beauty and diversity of European lakes make them popular destinations for recreation and tourism. Visitors can enjoy:
- Water sports:Swimming, boating, fishing, and kayaking are popular activities on many lakes.
- Scenic views:The stunning landscapes surrounding lakes offer breathtaking views for hiking, biking, and photography.
- Cultural heritage:Many lakes have historical and cultural significance, with castles, churches, and villages located along their shores.
European Rivers
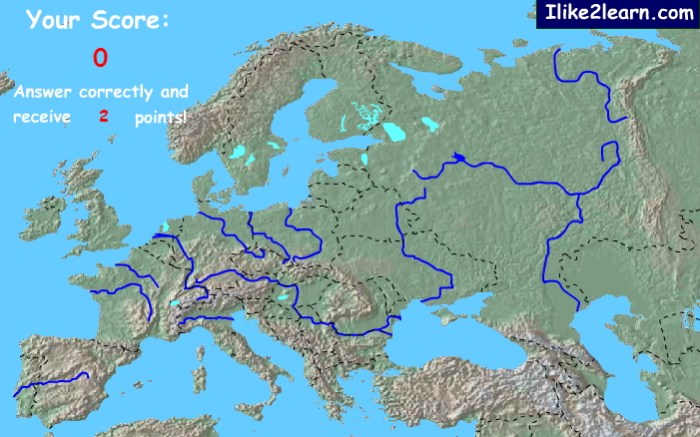
Europe is home to a vast network of rivers that have played a crucial role in shaping its history, culture, and economy. These rivers provide transportation, irrigation, and hydropower, and have served as boundaries and trade routes for centuries.
Major European Rivers
The major rivers of Europe include:
- Volga(3,690 km): Originates in the Valdai Hills of Russia and flows into the Caspian Sea.
- Danube(2,850 km): Originates in the Black Forest of Germany and flows into the Black Sea.
- Ural(2,428 km): Originates in the Ural Mountains and flows into the Caspian Sea.
- Dnieper(2,201 km): Originates in the Valdai Hills of Russia and flows into the Black Sea.
- Don(1,870 km): Originates in the Central Russian Upland and flows into the Sea of Azov.
- Rhine(1,233 km): Originates in the Swiss Alps and flows into the North Sea.
- Oder(854 km): Originates in the Sudeten Mountains of the Czech Republic and flows into the Baltic Sea.
- Elbe(727 km): Originates in the Krkonoše Mountains of the Czech Republic and flows into the North Sea.
- Vistula(1,047 km): Originates in the Carpathian Mountains of Poland and flows into the Baltic Sea.
- Loire(1,006 km): Originates in the Massif Central of France and flows into the Atlantic Ocean.
Historical, Cultural, and Economic Importance
European rivers have played a vital role in the development of human civilization. They have provided transportation routes for trade and exploration, and have been the sites of major battles and settlements. The banks of rivers have been home to some of the oldest and most important cities in Europe, including London, Paris, and Rome.
Rivers have also been a source of inspiration for artists, writers, and musicians. The Rhine River, for example, has been immortalized in countless works of art and literature, including the famous poem “The Lorelei” by Heinrich Heine.
Today, European rivers continue to be important for transportation, irrigation, and hydropower. They also provide recreational opportunities such as fishing, boating, and swimming.
Environmental Challenges
European bodies of water face a range of environmental challenges that impact their ecological health and human well-being. These challenges stem from various human activities and natural processes, leading to significant consequences for water quality, biodiversity, and ecosystem services.
Understanding the causes and consequences of these challenges is crucial for developing effective strategies to protect and restore European water resources.
Water Pollution
Water pollution is a major threat to European water bodies, primarily caused by industrial effluents, agricultural runoff, and sewage discharge. Pollutants such as heavy metals, pesticides, and nutrients enter water systems, impairing water quality and harming aquatic life.
- Causes:Industrial activities, agricultural practices, inadequate wastewater treatment
- Consequences:Eutrophication, fish kills, loss of biodiversity, human health risks
Climate Change
Climate change poses significant challenges to European water bodies. Rising temperatures lead to increased evaporation, reduced precipitation, and more frequent extreme weather events, such as droughts and floods.
- Causes:Greenhouse gas emissions, global warming
- Consequences:Water scarcity, altered river flows, habitat loss, coastal erosion
Overuse and Abstraction, European bodies of water quiz
Overuse and abstraction of water resources for human consumption, irrigation, and industrial purposes can deplete water bodies, leading to ecological degradation and conflicts over water allocation.
- Causes:Population growth, urbanization, agricultural expansion
- Consequences:Lower water levels, loss of wetlands, disruption of aquatic ecosystems
Invasive Species
Invasive species, introduced through human activities, can disrupt the ecological balance of water bodies. They compete with native species for resources, alter habitats, and spread diseases.
- Causes:Shipping, trade, aquarium releases
- Consequences:Loss of biodiversity, reduced ecosystem resilience, economic losses
FAQ Section: European Bodies Of Water Quiz
What is the largest lake in Europe?
Lake Ladoga
Which river flows through the most European countries?
Danube River
What is the deepest sea in Europe?
Norwegian Sea