Embarking on an intellectual odyssey with student exploration: evolution: natural and artificial selection, this comprehensive exploration delves into the profound significance of hands-on learning and real-world observations in fostering a deeper understanding of evolutionary processes. Through engaging activities and thought-provoking discussions, students will unravel the intricate mechanisms that drive evolutionary change, shaping the diversity and interconnectedness of life on Earth.
Delving into the principles of natural selection, we uncover the interplay of variation, inheritance, and differential survival in shaping populations. We will contrast this with the concept of artificial selection, examining its applications in agriculture and breeding, highlighting the similarities and differences between these two evolutionary forces.
Student Exploration: Evolution

Student exploration plays a crucial role in understanding the concept of evolution. Hands-on activities and real-world observations allow students to experience evolutionary processes firsthand, enhancing their comprehension and retention of the material.
For example, a simulated natural selection experiment using different colored beetles can demonstrate the impact of environmental pressures on the survival and reproduction of individuals. Students can observe how the beetles’ color adaptations affect their ability to avoid predators and find food, providing a tangible representation of the principles of natural selection.
Natural Selection: Processes and Mechanisms, Student exploration: evolution: natural and artificial selection
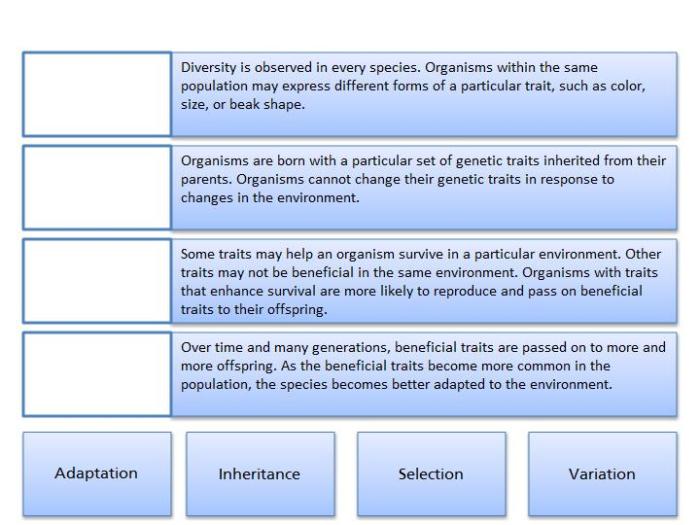
Natural selection is a driving force behind evolutionary change. It operates on three key principles: variation, inheritance, and differential survival.
Variation refers to the genetic diversity within a population. Inheritance ensures that these variations are passed on to offspring. Differential survival occurs when individuals with advantageous traits have a higher probability of surviving and reproducing, leading to the accumulation of beneficial traits over generations.
Artificial Selection: Human-Directed Evolution
Artificial selection is the intentional manipulation of breeding to produce desired traits in plants and animals. It involves selecting individuals with specific characteristics and breeding them together to create offspring with those traits.
Artificial selection differs from natural selection in that it is directed by human intervention. However, both processes share the principles of variation, inheritance, and differential survival.
Evidence for Evolution: From Fossils to Molecular Biology
Numerous lines of evidence support the theory of evolution, including:
- Fossil records:Fossilized remains provide a glimpse into the diversity and evolution of life over geological time.
- Comparative anatomy:Similarities in anatomical structures across species suggest common ancestry and evolutionary relatedness.
- Molecular biology:DNA and protein sequences reveal genetic relationships between species, providing insights into evolutionary history.
Evolution and Adaptation: Case Studies
Evolution results in the adaptation of species to their specific environments.
- Peppered moths:Industrial pollution led to the selection of dark-colored moths, providing camouflage against soot-covered trees.
- Antibiotic resistance in bacteria:Overuse of antibiotics has selected for bacteria that have evolved resistance mechanisms.
Evolution and the Human Experience
Evolution has profound implications for human understanding of our place in the natural world.
It challenges traditional views of human exceptionalism and raises ethical and societal considerations related to genetic engineering and the application of evolutionary principles in medicine and agriculture.
Frequently Asked Questions: Student Exploration: Evolution: Natural And Artificial Selection
What is the significance of student exploration in understanding evolution?
Hands-on activities and real-world observations provide students with a tangible and immersive experience of evolutionary processes, enhancing their comprehension and retention of complex concepts.
How does natural selection drive evolutionary change?
Natural selection operates through the interplay of variation, inheritance, and differential survival, favoring individuals with traits that enhance their adaptation to their environment.
What are the applications of artificial selection?
Artificial selection is employed in agriculture and breeding to selectively breed organisms with desired traits, leading to the development of new varieties of plants and animals.
What evidence supports the theory of evolution?
Fossil records, comparative anatomy, and molecular biology provide compelling evidence for the interconnectedness and diversity of life, supporting the theory of evolution.
What are the ethical considerations related to the study of evolution?
The study of evolution raises ethical questions regarding the applications of evolutionary principles in areas such as genetic engineering and reproductive technologies.