The student exploration ideal gas law provides a captivating gateway into the fascinating realm of gases, unveiling their fundamental principles and practical applications. By delving into the intricacies of pressure, volume, temperature, and number of moles, this exploration empowers students to unravel the enigmatic behavior of gases that shape our world.
This exploration extends beyond theoretical concepts, delving into real-world applications that showcase the versatility of the ideal gas law. From its indispensable role in chemistry and physics to its engineering applications, students will gain a profound appreciation for the law’s far-reaching impact.
Ideal Gas Law Principles
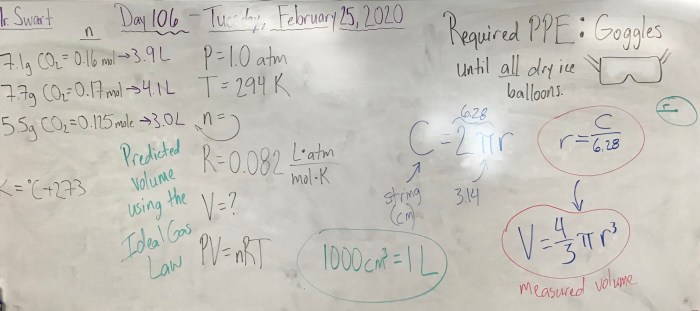
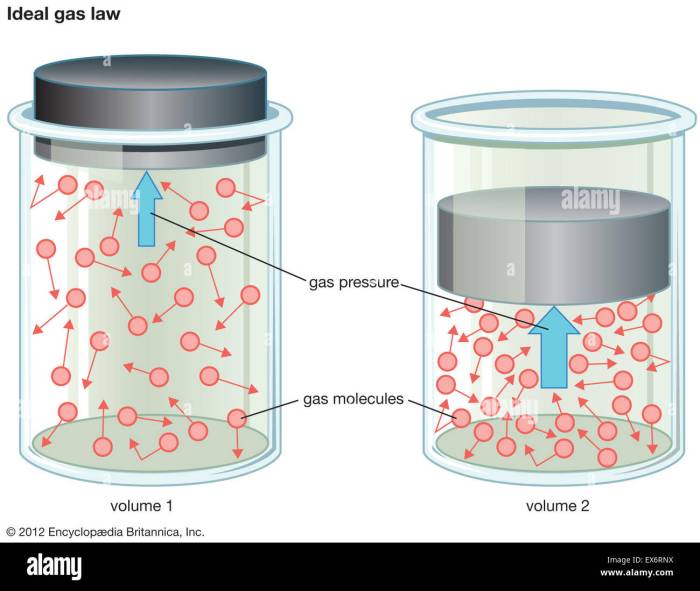
The ideal gas law is a fundamental equation that describes the behavior of gases under various conditions. It is based on the assumption that gas particles are point masses that do not interact with each other. The ideal gas law equation is given by:PV = nRTwhere P is the pressure of the gas, V is the volume of the gas, n is the number of moles of gas, R is the ideal gas constant, and T is the temperature of the gas.The
ideal gas law can be used to solve a variety of problems involving gases. For example, it can be used to calculate the pressure of a gas when its volume and temperature are known, or to calculate the volume of a gas when its pressure and temperature are known.
Applications of the Ideal Gas Law
The ideal gas law is used in a wide variety of fields, including chemistry, physics, and engineering. In chemistry, the ideal gas law is used to calculate the molar mass of a gas, to determine the density of a gas, and to calculate the partial pressure of a gas in a mixture.
In physics, the ideal gas law is used to calculate the speed of sound in a gas, to determine the thermal conductivity of a gas, and to calculate the specific heat of a gas. In engineering, the ideal gas law is used to design engines, turbines, and other devices that use gases.
Limitations and Assumptions of the Ideal Gas Law
The ideal gas law is a simplified model of gas behavior. It assumes that gas particles are point masses that do not interact with each other. This assumption is not always valid, especially at high pressures and low temperatures. At these conditions, gas particles can interact with each other, and the ideal gas law does not accurately predict the behavior of the gas.
Student Exploration Activities
There are a number of hands-on experiments that can be used to demonstrate the principles of the ideal gas law. One simple experiment is to measure the pressure of a gas as its volume is changed. This experiment can be used to show that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume.
Visualizations and Simulations, Student exploration ideal gas law
There are a number of interactive simulations and visualizations that can be used to explore the ideal gas law in a dynamic way. These simulations can be used to show how the pressure, volume, temperature, and number of moles of a gas are related to each other.
Answers to Common Questions: Student Exploration Ideal Gas Law
What is the ideal gas law?
The ideal gas law is a mathematical equation that describes the behavior of gases under certain conditions, assuming they behave ideally. It relates pressure, volume, temperature, and number of moles of a gas.
How is the ideal gas law used in real-world applications?
The ideal gas law finds applications in various fields, including chemistry, physics, and engineering. It is used to calculate gas properties, design gas-based systems, and predict the behavior of gases in different scenarios.
What are the limitations of the ideal gas law?
The ideal gas law assumes gases behave ideally, which is not always the case in reality. Deviations from ideal behavior occur at high pressures and low temperatures, where gas particles exhibit non-ideal interactions.