Generation genius rocks and minerals – Generation Genius: Rocks and Minerals embarks on a captivating journey into the realm of geology, unveiling the intricacies of rocks and minerals through the lens of the innovative Generation Genius platform. This comprehensive guide empowers readers with a profound understanding of these natural wonders, fostering a deep appreciation for their beauty, diversity, and practical applications.
Rock and Mineral Classification: Generation Genius Rocks And Minerals
Rocks and minerals constitute the solid components of the Earth and play a pivotal role in various geological processes. A comprehensive understanding of their classification aids in identifying, studying, and utilizing these natural resources effectively.
Rocks and minerals exhibit distinct characteristics based on their composition, structure, and properties. This diversity necessitates a systematic classification system to organize and categorize them. The primary distinction lies between rocks and minerals, with the former representing solid aggregates of minerals and the latter referring to naturally occurring inorganic substances with a definite chemical composition and crystalline structure.
Rock Classification
Rocks can be classified into three main categories based on their mode of formation: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic.
| Rock Type | Composition | Structure | Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| Igneous | Formed from the cooling and solidification of molten rock (magma or lava) | Crystalline or glassy | Hard, dense, and durable |
| Sedimentary | Formed from the accumulation and compaction of sediments (fragments of rocks, minerals, or organic matter) | Layered or clastic | Soft, porous, and easily weathered |
| Metamorphic | Formed from pre-existing rocks that have undergone physical and chemical changes due to heat, pressure, or chemical alteration | Crystalline or foliated | Variable, depending on the parent rock and metamorphic conditions |
Generation Genius Platform
The Generation Genius platform is a comprehensive online resource for studying and identifying rocks and minerals. It provides a wealth of tools and resources to assist users in their research and learning.
Tools and Resources
The Generation Genius platform offers a range of tools and resources for rock and mineral analysis, including:
- An extensive database of rock and mineral specimens, with detailed descriptions and high-quality images.
- Interactive identification tools, such as a mineral streak plate and a hardness tester, to help users identify unknown specimens.
- Educational resources, such as articles, videos, and quizzes, to enhance understanding of rock and mineral science.
User Interface and Functionality
The Generation Genius platform has a user-friendly interface and intuitive functionality, making it easy to navigate and use. The platform is accessible through a web browser and can be used on a variety of devices, including computers, tablets, and smartphones.
The platform’s home page features a search bar, which can be used to search for specific rocks or minerals, as well as a menu bar with links to the various sections of the platform, including the database, identification tools, and educational resources.
The platform also includes a number of social features, such as the ability to create and share collections of specimens, and to participate in discussion forums with other users.
Rock and Mineral Identification
Identifying rocks and minerals is a crucial aspect of geology, allowing scientists to classify and understand the composition and origin of Earth’s materials. The Generation Genius platform provides a comprehensive suite of tools and resources to facilitate accurate rock and mineral identification.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Acquire a sample:Obtain a small, representative sample of the rock or mineral to be identified.
- Observe physical properties:Examine the sample’s color, luster, hardness, cleavage, and other physical characteristics. Record these observations carefully.
- Use the search tool:Navigate to the Generation Genius website and use the search bar to enter specific physical properties or s related to your observations.
- Filter the results:The platform will display a list of potential matches. Use the filtering options to narrow down the results based on additional criteria, such as chemical composition or crystal structure.
- Interpret the results:Compare the physical properties of your sample to the information provided for each potential match. Consider the likelihood of the mineral or rock occurring in the geological context where the sample was collected.
- Make an identification:Based on the comparison and analysis, select the most likely match as the identification of your rock or mineral.
Tips for Accurate Identification
- Pay attention to details: Observe the physical properties of your sample carefully and accurately.
- Use multiple criteria: Consider various physical and chemical properties to increase the accuracy of your identification.
- Compare with known samples: If possible, compare your sample to known or reference samples to confirm your identification.
- Seek expert advice: If necessary, consult with a geologist or other expert for assistance in identifying complex or unusual samples.
Rock and Mineral Properties
Rocks and minerals possess distinct physical and chemical properties that aid in their identification and classification. These properties include hardness, luster, color, and cleavage, among others.
Hardness, a measure of a mineral’s resistance to scratching, is determined using the Mohs scale. Minerals are assigned a hardness value from 1 (talc) to 10 (diamond). Luster, the way light interacts with a mineral’s surface, can be metallic, non-metallic, or earthy.
Color, though often variable, can provide clues about a mineral’s composition.
Cleavage and Fracture
Cleavage refers to a mineral’s tendency to break along specific planes of weakness, resulting in smooth, flat surfaces. Fracture, on the other hand, describes irregular breakage patterns. Cleavage and fracture can aid in mineral identification.
| Property | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | Resistance to scratching | Talc (1), Quartz (7), Diamond (10) |
| Luster | Interaction of light with surface | Metallic (galena), Non-metallic (quartz), Earthy (kaolinite) |
| Color | Apparent color in visible light | Red (garnet), Green (malachite), White (calcite) |
| Cleavage | Breakage along specific planes | Perfect (calcite), Imperfect (quartz), None (diamond) |
| Fracture | Breakage along irregular surfaces | Conchoidal (flint), Splintery (wood), Uneven (granite) |
Understanding these properties is crucial for distinguishing between different types of rocks and minerals. By observing and analyzing these characteristics, geologists and mineralogists can identify and classify rocks and minerals, providing valuable insights into their composition, formation, and geological significance.
Rock and Mineral Formation
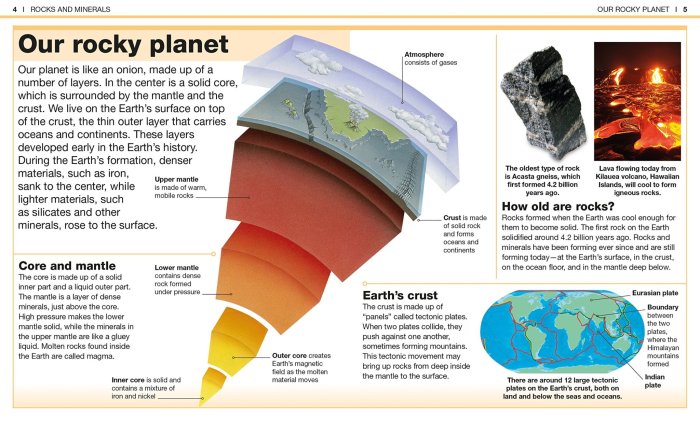
Rocks and minerals are formed through a variety of geological processes that occur over millions of years. These processes involve the interaction of various forces, such as heat, pressure, and chemical reactions, with different types of materials.
Weathering and Erosion
Weathering is the process of breaking down rocks and minerals into smaller pieces. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including temperature changes, exposure to water, and the action of wind and ice. Erosion is the process of transporting these smaller pieces away from their original location.
Deposition, Generation genius rocks and minerals
Deposition is the process of depositing these smaller pieces in a new location. This can occur in a variety of environments, such as rivers, lakes, and oceans. Over time, these deposited materials can accumulate and form new rocks.
Metamorphism
Metamorphism is the process of changing the mineral composition and texture of a rock. This can occur when a rock is subjected to high temperatures and pressures. Metamorphism can also occur when a rock is chemically altered by fluids.
Types of Geological Environments
Rocks and minerals are formed in a variety of geological environments, including:
- Igneous rocks are formed from the cooling and solidification of molten rock (magma or lava).
- Sedimentary rocks are formed from the accumulation and compaction of sediments, such as sand, mud, and gravel.
- Metamorphic rocks are formed from the alteration of existing rocks by heat, pressure, or chemical reactions.
Flowchart of Rock and Mineral Formation
The following flowchart illustrates the various stages of rock and mineral formation:
- Weathering and erosion break down rocks and minerals into smaller pieces.
- These smaller pieces are transported and deposited in a new location.
- Over time, these deposited materials can accumulate and form new rocks.
- These new rocks can be subjected to heat, pressure, and chemical reactions, which can alter their mineral composition and texture.
- This process can result in the formation of metamorphic rocks.
Rock and Mineral Uses

Rocks and minerals are essential resources with diverse applications across various industries. Their unique physical and chemical properties make them indispensable for a wide range of products and technologies.
Construction
Rocks such as granite, limestone, and marble are widely used as building materials due to their strength, durability, and aesthetic appeal. Granite is particularly valued for its use in countertops, flooring, and exterior cladding. Limestone is commonly used in construction as a building stone and for making cement.
Manufacturing
Minerals such as iron ore, copper, and aluminum are essential raw materials for the manufacturing industry. Iron ore is used to produce steel, which is used in construction, transportation, and manufacturing. Copper is used in electrical wiring, plumbing, and electronics.
Aluminum is used in aircraft, automobiles, and food packaging.
Jewelry
Certain minerals, such as diamonds, rubies, and sapphires, are highly prized for their beauty and rarity. They are used in jewelry and other decorative applications. Diamonds are the hardest known natural material and are often used in cutting tools and abrasives.
Economic and Societal Importance
Rocks and minerals play a crucial role in the global economy. The mining and processing of these resources generate significant revenue and employment. They are also essential for the development of infrastructure, transportation, and energy production. The availability and accessibility of rocks and minerals are critical factors in the economic prosperity and technological advancement of societies.
Essential FAQs
What is the Generation Genius platform?
Generation Genius is an innovative platform that provides a comprehensive suite of tools and resources for studying and identifying rocks and minerals.
How can I use the Generation Genius platform to identify rocks and minerals?
The platform offers a step-by-step guide, search and filtering tools, and detailed results to assist in accurate rock and mineral identification.
What are the key properties of rocks and minerals?
Rocks and minerals possess distinct physical and chemical properties, including hardness, luster, color, and cleavage, which can be used to distinguish between different types.
